Are you curious about laser cutting machine how does it work? Look no further! Laser cutting has revolutionized various industries, from manufacturing to art and design, by offering a highly efficient and accurate method of cutting a wide range of materials. Whether you’re an enthusiast or an industry professional, prepare to be amazed by the wonders endless possibilities of laser cutting application.
How Does a Laser Cutter Work?
When the laser beam is directed onto the surface of the work piece, the optical energy is absorbed and converted into thermal energy, causing the temperature of the illuminated spot to rise rapidly. This leads to melting and vaporization, resulting in a depression. Due to the effect of thermal diffusion, the surrounding metal around the spot is melted, and the metal vapor inside the small depression rapidly expands, creating a micro-explosion. This causes the molten material to be ejected at high speed, generating a highly directional shockwave, thereby creating a perforated and processed surface.
The specific laser cutting process is as follows:
1. Laser Generation
Utilize a laser generation device to produce a high-intensity laser beam.
2. Laser Import
Transmit the generated laser beam into the laser cutting machine through an optical fiber.
3. Positioning and Focusing
Use a positioning system to locate the cutting position and focus the laser beam to a very small point using a focusing lens.
4. Material Cutting
When the laser beam irradiates the material, the high temperature causes the material to melt or evaporate. The material is then cut into the desired shape by moving the cutting head.
5. Cooling and Exhaust
During the cutting process, heat accumulates on the cutting head. Therefore, a cooling system is required to reduce the temperature, and an exhaust system is used to remove the generated smoke.
This is the working principle of a laser cutting machine, which can be applied to cut various materials such as steel plates, aluminum sheets, plastics, fabrics, wood, ceramics, etc.
How to Get Started with Laser Cutting Machine Step by Step?
Here is a 7 steps guide to help you begin laser cutting and manufacturing:
1. Design drawing: It is necessary to design the drawing and convert it into data using CAD, CorelDraw or other design software.
2. File conversion: Convert the designed data into files recognized by the laser cutting machine, such as DXF, PLT and other formats.
3. Load material: Place the material to be cut on the worktable of the laser cutting machine and keep its surface flat through fixtures or air cushions.
4. Laser cutting parameters setting: Before laser cutting, it is necessary to perform calibration of the laser cutting machine to ensure cutting accuracy and quality. Then set laser power, speed, focus position and other parameters according to the type and thickness of the material.
5. Start cutting: Turn on the power of the fiber laser cutting machine, start the cutting software, and input the required cutting pattern and parameter information. After pressing the start cutting button, the machine will start cutting.
6. Finish cutting and remove material: After cutting is completed, take out the cut parts and materials from the work platform when the laser cutting machine stops working and clean the worktable through cleaning and dust removal, etc.
7. Cleaning: Clean the working environment of the laser cutting machine and check if the machine has any faults.
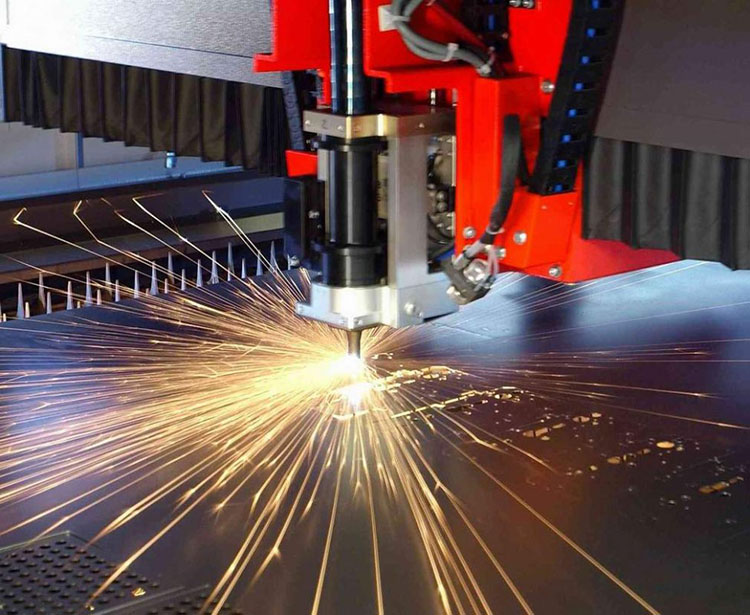

Remember, safety is paramount when working with laser cutting machines. Always follow proper safety protocols, wear appropriate protective gear, and consult the machine’s user manual for specific safety guidelines.
By following these steps, you can confidently get started with your fiber laser cutting machine and explore creative possibilities. For more working details, please refer to the article Laser Cutting Basics.
Fiber Laser Cutting vs. Traditional Cutting
1. Good Cutting Quality
Due to the small laser spot, high energy density, and fast cutting speed, laser cutting can achieve good cutting quality. Laser cutting has extremely high positioning accuracy, with cutting dimensional accuracy reaching 0.01mm, and the cut shapes and contours are very precise. After laser cutting, the heat-affected zone is narrow, and the performance of the material near the cut is hardly affected. The workpiece deformation is minimal, with high cutting accuracy and good geometric shape of the cut, presenting a regular rectangular cross-sectional shape.
2. High Level of Automation
Laser cutting adopts CNC and automated control, enabling highly automated production processes to improve production efficiency, labor saving and enhance processing quality.
3. Fast Cutting Speed
Laser cutting is fast, providing high work efficiency. For example, using a 1200W laser power to cut 2mm thick low carbon steel, the cutting speed can reach 600cm/min. Materials of different thickness and hardness will have different cutting speeds. Do not require clamping or fixing during laser cutting, saving on fixtures and auxiliary time for loading and unloading.
4. Non-contact Cutting
During laser cutting, there is no contact between the cutting tool and the workpiece, eliminating tool wear. When processing parts of different shapes, there is no need to change accessories, only the output parameters of the laser need to be adjusted. Laser cutting is a pollution-free, noiseless, and vibration-free cutting method. It does not generate exhaust gas, wastewater, or residue, making it an environmentally friendly and energy-saving processing technology.
5. Wide Cutting Range
Laser cutting technology can cut various materials such as metals, plastics, wood, leather, textiles, etc. It can also cut small and complex patterns and curves.
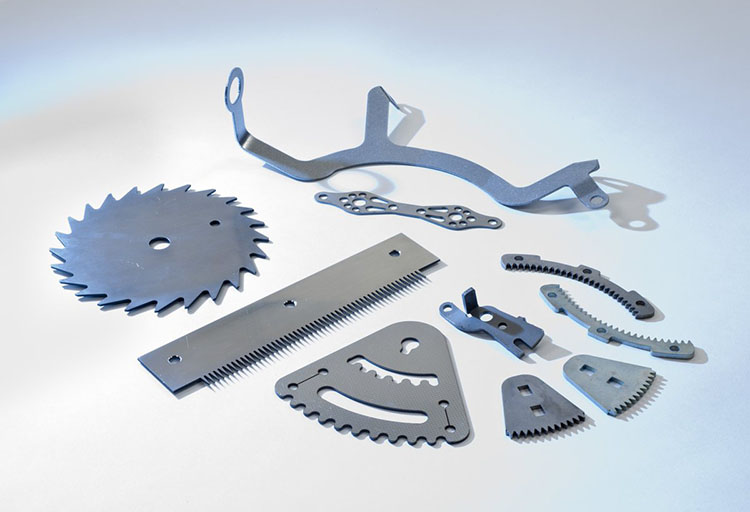

Cons.
Due to the limitations of laser power and equipment size, laser cutting can only cut medium and small thickness plates and tubes. Moreover, as the thickness of the workpiece increases, the cutting speed significantly decreases. Laser cutting equipment is costly, requiring a substantial one-time investment.
Fiber laser cutting is often favored for its superior speed, precision, versatility, and efficiency. However, traditional cutting methods still have their place in certain applications where specific materials or cutting requirements.
Why Laser Cutting Uses Auxiliary Gas?
Laser cutting utilizes the high temperature and energy of the laser beam to process materials. Since laser cutting is carried out in an oxidizing environment, not using any auxiliary gas will cause a large amount of oxidative waste and rough cutting surfaces. To solve these problems, auxiliary gases such as nitrogen, oxygen and inert gases (such as argon) are commonly used in laser cutting. These gases can cool and protect the cutting area, prevent oxidation and chemical reactions, and make the cutting surface fine and smooth. The auxiliary gas can also increase the cutting speed and improve the cutting quality, so using auxiliary gas in the laser cutting process can improve production efficiency and product quality.
What are the Different Types of Laser Cutting Machines?
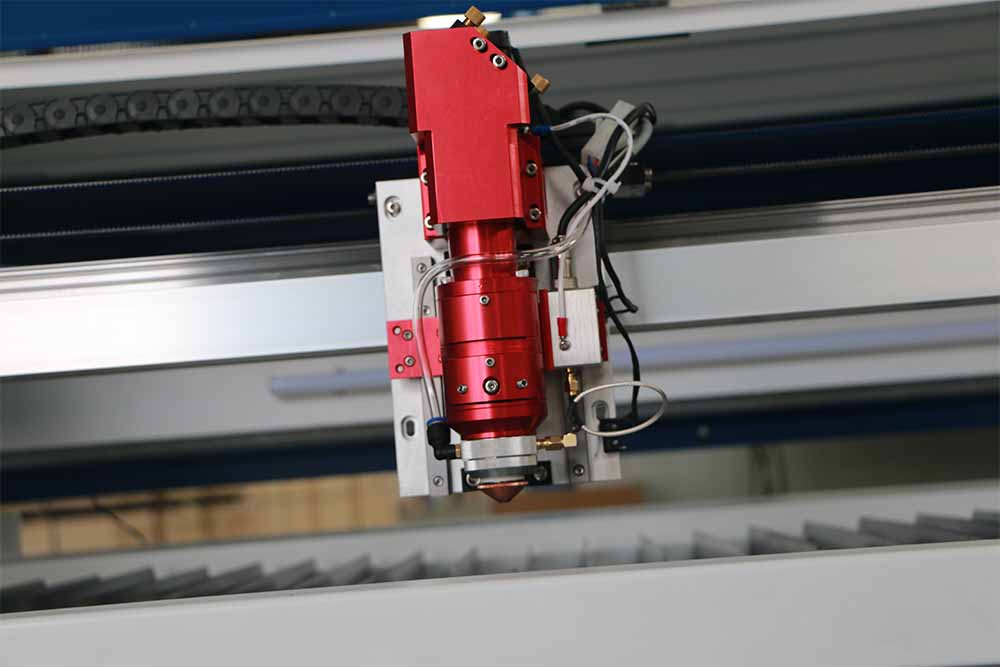
The laser source of a laser cutting machine originates from the laser resonator, which emits a high-intensity beam of light through a reflection mirror system towards the cutting head. Inside the cutting head, the laser is focused and reduced to an extremely fine, concentrated beam of light through a lens. This beam can be projected downwards onto the material to cut or rasterize it. The cutting head is typically mounted on an XY gantry and allows the cutting head to move within a given rectangular area that matches the size of the worktable, so that it can perform precision cutting anywhere on the bed.
Fiber laser cutters share a similar construction, but their differentiation lies in the specific power range of each type of laser, enabling them to cut through different materials of varying thicknesses.
1. CO2 Laser Cutters
CO2 lasers are the most popular type of laser cutter. They use a gas mixture, typically carbon dioxide, as the laser medium. CO2 laser cutters are best suited for cutting non-metal materials like wood, acrylic, plastics, and fabrics.

2. Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
Fiber lasers are a newer type of laser technology that uses a solid-state laser medium to generate the laser beam. Fiber lasers are highly efficient and can cut through metal and non-metallic sheet and pipe with high precision.

3. Nd:YAG Laser Cutters
Nd:YAG lasers use a crystal medium made of neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet. They are best suited for cutting thick metal sheets and are often used in industrial applications.
4. UV laser Cutting Machine
UV laser cutters use a higher frequency laser beam than traditional CO2 lasers and are used for cutting and engraving materials like glass, ceramics, and semiconductors.
5. Green Laser Cutters
Green lasers use a green light wave to produce a laser beam, which is ideal for cutting thicker materials like metals and glass.
The type of laser determines the type and thickness of material it can cut, as different laser types have different power ranges. Generally, higher power fiber lasers are used in industrial manufacturing to cut high-hardness, high-thickness metal plates or plastics. While lower power CO2 laser and UV laser are used to cut a variety of thinner materials such as paper, wood, glass, acrylic and plastic.
What is the Difference between Laser Cutting and Laser Engraving?
Laser cutting and laser engraving are two machining methods based on laser technology.
Laser cutting is the process of cutting materials using a laser beam. The laser beam is focused on a small area of the material with high energy density, causing rapid heating and melting or vaporization of the material, thus achieving the cutting process. Laser cutting is widely used in the processing of metals, plastics, wood, textiles, and other materials, and can be used for cutting straight lines, curves, and complex shapes.
Laser engraving is the process of etching and marking the surface of a material using a laser beam. The energy of the laser beam increases the temperature of a localized area on the material’s surface, thereby changing the color, texture, or surface properties of the material and forming patterns, text, or images. Laser engraving is suitable for materials such as wood, leather, glass, plastics, and stone, and can achieve high precision and high definition engraving effects.

The main differences are as follows:
1. Processing principles: Laser cutting involves cutting materials by high energy density, while laser engraving involves etching the material’s surface by adjusting the laser beam’s power and duration.
2. Processing effects: Laser cutting typically produces cutting edges, while laser marking focuses more on the surface marks and changes.
3. Application scope: Laser cutting is widely used for cutting various materials, while laser engraving is mainly used for carving patterns, text, or images for decorative purposes.
4. Energy requirements: Laser cutting generally requires higher laser power and energy, while laser etching has lower power and energy requirements.
The specific applications and effects are also influenced by factors such as the materials used, laser parameters, and equipment performance.
Laser Cutter Maintenance Guide
1. Daily Check: Daily checks on the working environment of the laser cutting machine to identify any abnormal conditions or issues.
2. Cleaning: Regularly clean the working environment of the laser cutting machine to prevent dust accumulation that could potentially damage the machine.
3. Maintenance: Conduct regular maintenance on the laser cutting machine, such as oil replacement and cleaning of the cooling system.
4. Component Replacement: If any components of the laser cutting machine malfunction, they should be promptly replaced to ensure the normal operation.
5. Repairs: In case of any malfunctions or breakdowns in the laser cutting machine, it should be stopped and repaired in time.
To ensure the smooth operation and lifespan of the laser cutting machine, adjustments and optimizations should be made according to the specific circumstances. Operators should be familiar with the user manual and laser cutting machine maintenance procedures and regular training to enhance their skills and knowledge.
What can Laser Cutting Do?
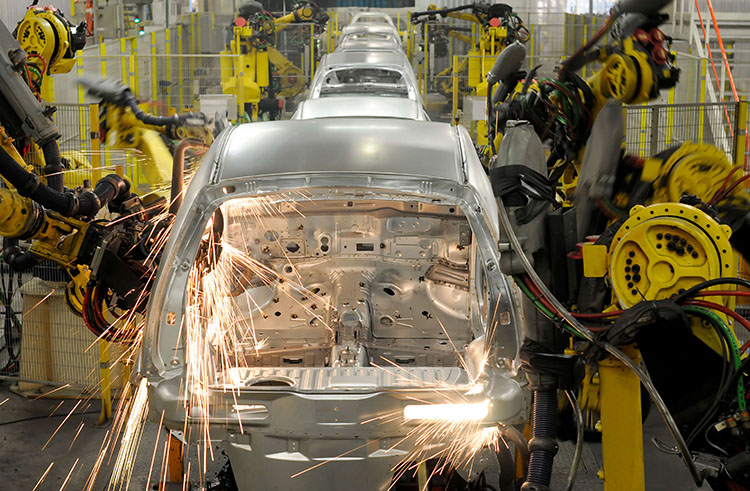
Automobile Manufacturing
In the field of automobile manufacturing, laser cutting has been widely applied to curved spaces such as car sunroofs. Volkswagen AG, for instance, utilizes laser cutters to cut complex-shaped body panels and various curved components.

Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, fiber laser cutting technology is primarily used for cutting special aerospace materials such as titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, nickel alloys, chromium alloys, stainless steel, beryllium oxide, composite materials, plastics, ceramics, and quartz. Aerospace components processed through laser cutting include engine flame tubes, thin-walled titanium alloy casings, aircraft frames, titanium alloy skins, wing spars, tail planes and helicopter main rotors.
Non-Metal Processing
Laser cutting technology also finds extensive application in the non-metal materials. It can cut high hardness and brittle materials such as silicon nitride, ceramics, quartz, as well as flexible materials like fabrics, paper, plastic sheets, rubber, etc. For example, laser cutting can significantly reduce waste by 10% to 12% and improve work efficiency in clothing cutting.
Let the automatic laser cutting machine transform your production. Now that you understand how laser cutting machine works and the advantages they bring, you can realize the benefits they offer to your manufacturing process. Laser cutting provides you with great design flexibility and enables you to achieve optimal production results.
Custom Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
At DPLASER, we take pride in providing not only high-quality laser cutting machines but also customized laser cutter services to meet your specific needs. We understand that every project and application is unique, and our team of experts is dedicated to delivering personalized solutions that align with your requirements.
In conclusion, the laser cutting machine process is a remarkable feat of engineering and innovation. Its ability to precisely cut through various materials with incredible speed and accuracy has revolutionized industries around the world. From intricate designs in jewelry and automotive parts to intricate patterns in textiles and signage, laser cutting machines have become an indispensable tool for manufacturers, artisans, and designers alike. If you have any further insights or would like to learn more about laser cutting, feel free to leave a comment, reach out via email, or connect with us on social media.




