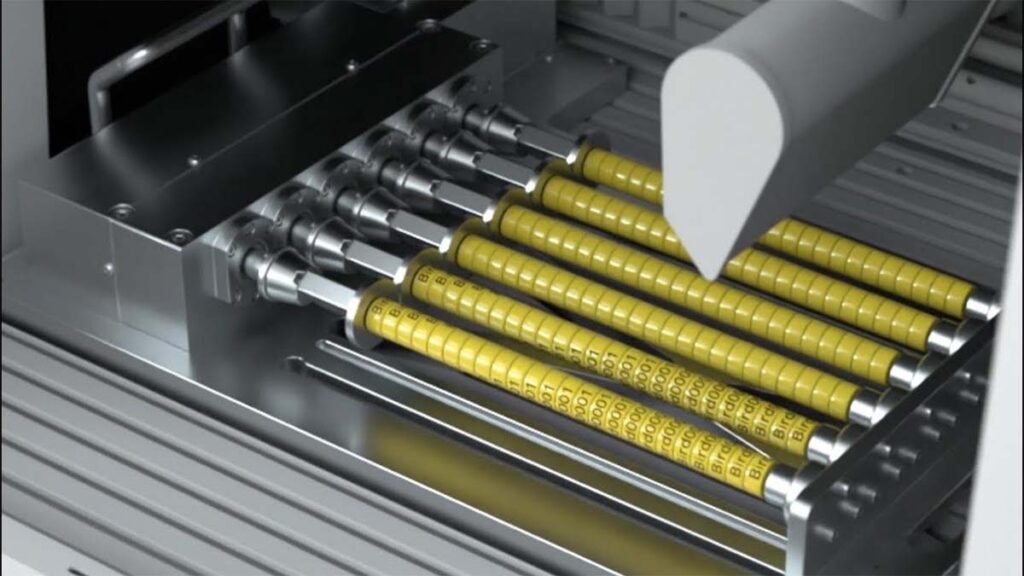
Laser marking is a non-contact technique used to leave permanent marks on the surface of parts. Using lasers, you can easily create various designs and patterns on materials in a short amount of time. This method is fast, enhancing production efficiency. Since the process is non-contact, the physical properties of the materials remain unchanged, making laser technology highly popular in manufacturing industries. The quality of laser marking directly depends on the parameters of laser marking.
These parameters have complex interrelationships, and appropriate selection can achieve high-quality marks, while improper selection can result in blurred marks, excessive ablation, or insufficient depth. The following are some factors of laser marking.
What Affects Laser Marking?
Laser Parameters:
– Power: the intensity of the laser will directly affect the marking effect, the higher the power, the faster the marking speed and the deeper the marking depth may be, but it may also lead to excessive ablation or material damage.
– Pulse width: the duration of the pulsed laser, different materials and marking effects require different pulse widths.
– Wavelength: For different materials, it is necessary to choose the appropriate laser wavelength to ensure that the beam is better absorbed.
– Repetition frequency: the number of times the pulse is repeated, which affects the marking speed and marking depth. Some products need deep engraving, you can choose to increase the laser power current, or reduce the marking speed.
Generally for hard materials, you can choose a higher pulse frequency to improve the marking accuracy; while for soft materials, you can moderately reduce the pulse frequency to avoid excessive ablation.

Scanning Parameters:
– Scanning speed: the speed at which the laser head moves affects the processing time and quality of the marked area, and too fast a scanning speed may cause unclear results.
– Focus size: the size of the focus point formed after the laser focus, affecting the fine degree of marking lines and processing depth.
– Focus position: the choice of laser focus position directly affects the focus of laser energy, a reasonable focus position can ensure that the laser energy is fully concentrated on the surface of the workpiece, thus improving the clarity and accuracy of marking.
Marking Density
With the same marking area, spot size, and depth, higher marking density results in slower marking speed. This is because increased density directly increases the marking area.
Marking Area
For larger marking areas, the deflection area of the galvanometer is larger, so the marking speed for larger areas is slower compared to smaller areas. Increasing the laser power or reducing the speed can solve this problem. If you need deep engraving, a marking size of 100*100mm is optimal.
Laser Spot Size
In laser marking technology, the spot size directly affects the precision and speed of marking. A smaller spot size means that the laser energy is more concentrated, enabling finer markings. However, for the same marking area, a smaller spot size leads to higher marking density and slower marking speed.
Material properties:
– Material type: Different materials (e.g. metal, plastic, ceramic, etc.) have different absorption rates of laser light, which affects the marking effect.
– Color and texture: The color and surface treatment of the material itself will affect the laser absorption and reflection.
– Surface condition: Smooth and rough surfaces lead to different laser scattering and absorption effects.
Laser Wavelength
For the same material, the wavelength of a laser marking machine affect the color of the mark. Fiber lasers have a wavelength of 1064nm, CO2 lasers typically have a wavelength of 10,600nm, and ultraviolet (UV) lasers have a shorter wavelength, usually around 355nm. When laser marking on ABS plastic, CO2 lasers produce a yellowish mark, fiber or semiconductor lasers produce a grayish-black mark, and UV or green lasers produce a black mark.
What are the Differences between Laser Marking on Metal and Non-Metal Materials?
On metallic materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass and copper.
- High-power lasers can deliver enough energy in a short period of time to melt and vaporize the metal surface, producing a clear mark.
- However, to ensure sufficient energy is delivered to the surface, it is often necessary to select a relatively slow marking speed.
- In addition, high pulse frequencies can help improve marking accuracy, but need to be adjusted to the thermal conductivity of the metal to avoid overheating.
- Finally, the focal position on the metal surface is usually chosen at the surface of the material to ensure that the laser can be focused sufficiently on the surface to achieve accurate marking results.


Factors Affecting the Laser Marking For Non-Metal Materials
- For non-metallic materials such as plastics and glass, lower laser powers are selected to avoid excessive ablation and thermal damage.
- Faster marking speeds, as non-metallic materials have a lower absorption capacity, can be sped up without damaging the material.
- Lower pulse frequency and moderate pulse width are usually chosen to prevent excessive ablation and damage.
- The focus position is usually chosen at the surface or at a moderate depth, depending on the specific material type, to ensure that the laser can effectively act on the surface of the material or at the desired depth.


How to Set Parameters of Laser Blackening Stainless Steel?
- Adjust Speed: Reduce the movement speed of the laser head. Slower speeds help concentrate energy more effectively on the material surface, promoting the formation of a blackening effect.
- Increase Current: Raise the operating current of the laser to enhance energy output, which aids in deepening the color and achieving a darker effect.
- Choose High-Frequency Mode: Use a high-frequency setting between 60 to 80 kHz. High frequencies allow for denser laser pulses, facilitating the formation of fine and uniform marking effects on the material surface, beneficial for generating black color.
- Employing an out-of-focus strategy: marking slightly out of the optimal focal position helps to change the energy distribution and sometimes promotes deeper discoloration of the material to achieve the desired black effect.
- Power Adjustment: Adjust laser power as needed; generally, higher power results in darker markings. However, caution is necessary to avoid overheating or damaging the material.
- Set Spacing: Reduce the distance between laser points to create more continuous and deeper coloration in the marking area. Closer spacing enhances energy absorption per unit area, thereby deepening the color.
- Equipment Selection: Opt for a MOPA fiber laser marker. This type of laser is well-suited for precise blackening treatments on stainless steel and various other metal surfaces due to its excellent pulse width and frequency adjustment capabilities. Materials include but are not limited to steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and anodized aluminum.
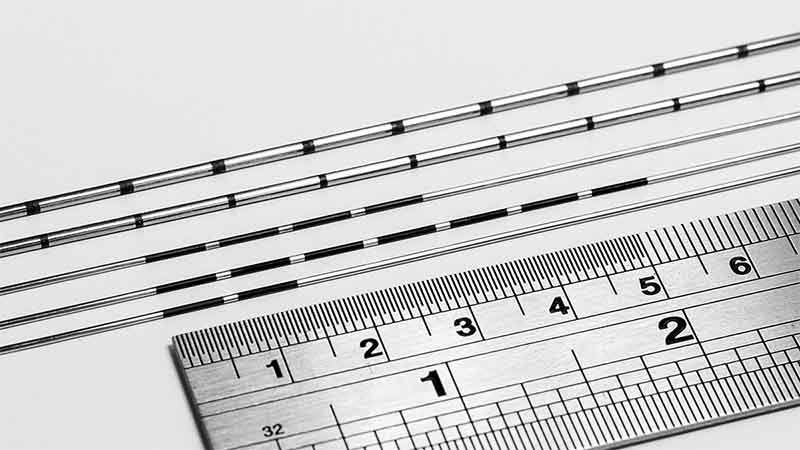


In summary, through fine adjustment of various parameters of the laser marking machine, such as speed, current, frequency, focal length, power and pitch. Combined with the use of a high-performance MOPA fiber laser, the ideal black marking effect can be achieved on stainless steel surfaces, while the marking depth is controlled by adjusting the speed to meet different processing needs.


To achieve the desired marking quality, the above parameters usually need to be considered together and well-adjusted and optimized. Engineers often set these parameters by trial and error or based on experience to achieve good marking results. Welcome to follow our laser technology articles or consult our equipment engineers for the best laser marking solutions.
Summary:
By understanding what affects laser marking and the application characteristics on different materials, we can better utilize this advanced technology to meet the needs of different industries. Laser marking not only provides highly accurate and long-lasting marks, but also brings significant advantages in terms of productivity and cost control. We hope that the information provided in this article will help you gain a more comprehensive understanding of the application of laser marking technology and its potential to add new possibilities to your business or project.



