In the industrial cleaning field, laser cleaning technology is becoming an efficient and eco-friendly solution. Pulsed laser and continuous laser are two common types of laser cleaning methods, each with its own advantages in principle and application. This article will detail the differences between pulsed laser and continuous laser cleaning, analyzing their working principles, application scenarios, and practical effects. This will help you better understand the distinctions between pulsed vs continuous laser cleaning and provide professional guidance for your choice. Whether you need to remove surface contaminants, oxide layers, or perform precise cleaning operations, this article will offer valuable reference information.
Laser cleaning uses a high-energy laser beam to precisely heat and vaporize or peel off contaminants instantly. This process ensures the cleanliness of the substrate surface while maintaining or restoring its smoothness, providing excellent conditions for subsequent processing steps. As an advanced alternative to chemical and mechanical cleaning methods, laser cleaning demonstrates significant advantages in the industrial cleaning sector due to its eco-friendliness, cost-effectiveness, and reduced labor requirements.
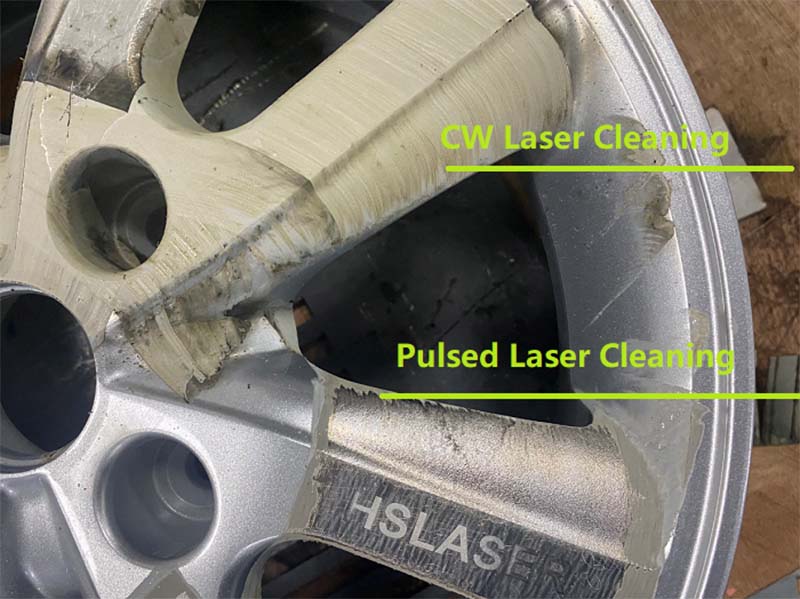
Difference between Pulsed Vs CW Laser Cleaning
Continuous Laser Cleaning
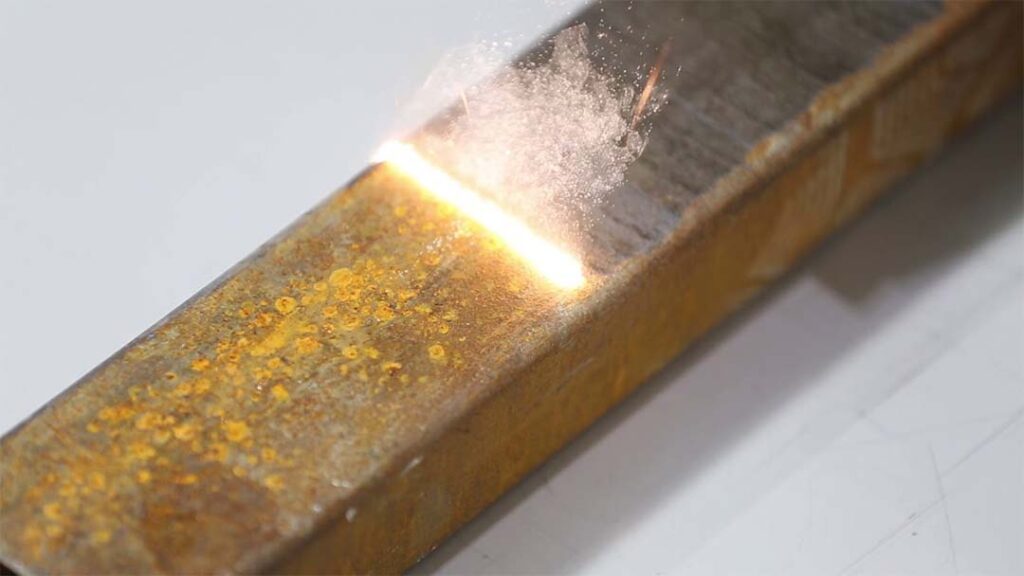
Continuous wave (CW) lasers emit a constant high-intensity laser beam at specific intervals. CW laser cleaning systems are suitable for heavy-duty cleaning tasks, such as removing rust from car bodies. Typically, these systems have higher output power, commonly ranging from 2000W to 3000W or more.
Pulsed Laser Cleaning
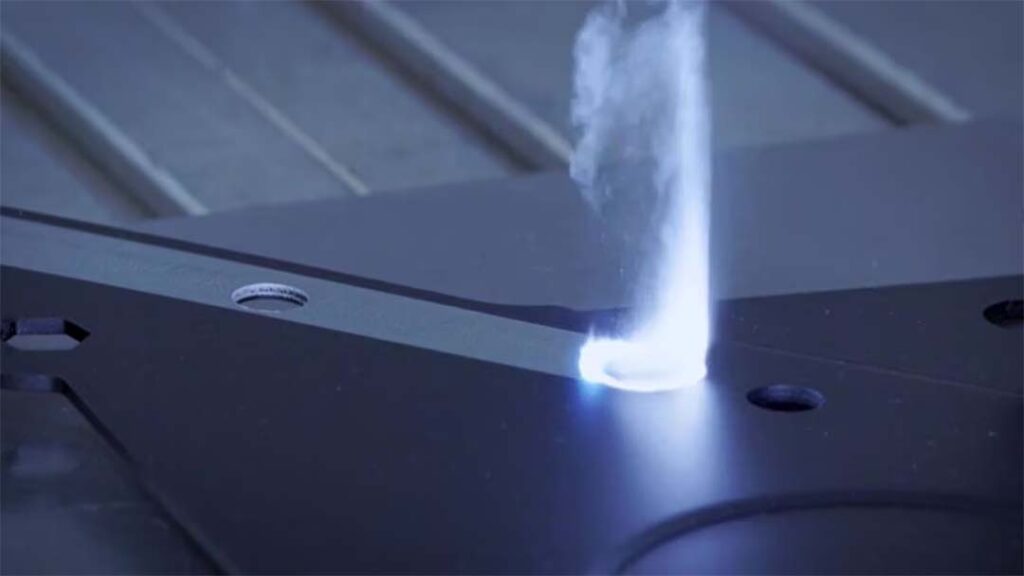
In pulsed laser mode, the equipment releases concentrated laser pulses at predetermined intervals. Each pulse delivers a burst of high-intensity light energy, followed by a return to a low-energy state before repeating. This mode is particularly suitable for cleaning sensitive materials because it effectively limits the thermal effect, minimizing heat damage and potential structural changes to the substrate, thereby preserving material integrity and performance. This is crucial for cleaning precision parts, thin-walled structures, or heat-sensitive electronic components. In industrial applications, handheld pulsed lasers with powers of 100W and 300W are commonly used to efficiently and precisely remove contaminants such as paint and grease from mold surfaces.


Advantages Pulsed Laser Cleaning Machine
- Non-Contact and Non-Damaging: Laser cleaning involves no physical contact, protecting delicate surfaces and offering a wide range of applications.
- High Precision and Selectivity: It accurately targets the contamination layer, preserving the substrate and meeting high-precision requirements.
- Environmentally Friendly: Reduces the use of chemicals, generates minimal waste, and ensures safe disposal.
- Efficient and Fast: Increases production efficiency and reduces downtime.
- Consistent Results: Ensures consistent cleaning quality and high standards.
- Adjustable Parameters: Laser parameters can be flexibly adjusted to suit various tasks.
- Wide Applications: Suitable for multiple materials and industries, such as manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive.
Pulsed vs CW laser cleaner for metal differ significantly in principles, applications, cleaning effectiveness, equipment costs, and operation.
Continuous Wave Laser Cleaner: These emit a continuous laser beam to heat the surface steadily, achieving a cleaning effect. The continuous laser provides a stable output of energy, resulting in a gentler cleaning action. Due to the lower temperature of continuous lasers, the cleaning effect is milder and not suitable for delicate or easily melted materials. However, continuous laser cleaning is effective for cleaning rougher surfaces.
Pro.
Continuous laser cleaners are usually suitable for cleaning large areas and materials with relatively flat surfaces. They have a relatively stable cleaning process, can work continuously, and have a relatively fast cleaning speed.
Cons.
For materials that are thin-walled, susceptible to thermal deformation or have special surface treatments, continuous laser cleaners may cause excessive heating or surface damage.


Pulsed Laser Cleaning Machine: These use high-energy, high-frequency laser pulses to heat and cool the surface rapidly, creating instantaneous temperature gradients and thermal stress. This causes contaminants and thin coatings to detach from the surface. The principle involves brief, high-energy pulses that generate high temperatures and pressures, quickly evaporating or breaking down contaminants, effectively cleaning the surface. Pulsed laser cleaning machines have minimal impact on the substrate, making them safer for cleaning various surfaces.
Pro.
High Peak Power: Provides extremely high peak power, making it more effective for handling tough or hard-to-remove materials.
Precise Control: Suitable for cleaning tasks requiring fine control, as the laser energy can be precisely focused on the target area, minimizing the impact on surrounding materials. Additionally, pulsed laser cleaning machines are more effective for complex surfaces, uneven objects, and tasks demanding higher precision.
Cons.
Higher Cost: Manufacturing and maintenance costs are typically higher compared to continuous laser cleaning machines.
Processing Speed: Due to intermittent emission, the processing speed for large-area cleaning tasks may be lower than that of continuous laser cleaning machines.


Industrial Applications of Pulse and Continuous Laser Cleaner
Metal:
Remove rust from steel
Remove paint and coatings from various metal surfaces
Removal of oxides and scale from metal parts
Weld cleaning and preparation of metal surfaces
Plastics:
Removing paint from plastic parts
Cleaning and removing coatings from plastic parts
Wood:
Removing paint or varnish from wooden surfaces
Restoration of wooden artefacts or furniture
Electronics and PCBs:
Removal of conformal coatings for rework and repair
Cleaning of electronic components, e.g. solder joints
Automotive:
Removing paint and coatings from bodywork and components
Removal of rust from vehicle frames and components
Marine Maintenance:
Remove marine dirt and paint from boat hulls


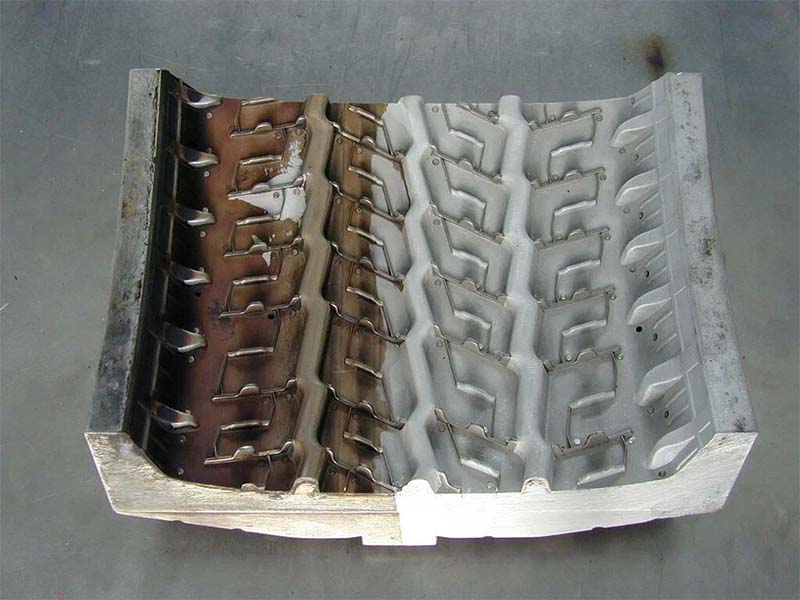
Cleaning Effect: Pulse and Continuous Laser Cleaner
Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine: Suitable for removing light contaminants adhering to surfaces, such as paint, grease, and dust. Ideal for cleaning large areas of flat surfaces.
Pulsed Laser Cleaning Machine: Ideal for tackling tougher residues like oxide layers, coatings, and welding spatter. Particularly suitable for cleaning tasks requiring high surface quality or precision components.
Both continuous and pulsed laser cleaners effectively remove surface contaminants from materials. Under equivalent power conditions, pulsed lasers clean more efficiently than continuous lasers and offer better control over heat input, preventing excessive substrate temperatures or micro-melting.
Continuous lasers are more cost-effective and can compensate for efficiency gaps with pulsed lasers by using high-power lasers. However, higher power continuous lasers generate more heat input, potentially increasing substrate damage.
For applications demanding high precision and strict control over substrate heating, such as molds, pulsed lasers are recommended. For larger steel structures, pipelines, etc., where heat dissipation is rapid and substrate damage tolerance is higher, continuous lasers may be preferable.
The choice between these laser cleaning types should consider factors such as the material being cleaned, precision requirements, and project budget.
How to Choose the Best Pulsed Laser Cleaning Machine?
This handheld laser cleaning machine swiftly removes contaminants such as dust, coatings, paint, and oil stains from workpiece surfaces. Designed for handheld operation, it is user-friendly and lightweight for easy portability. Users can grip the cleaning gun as needed to target specific areas, effectively cleaning flat, curved, and intricate geometries from various angles and material.
100W Pulsed Laser Cleaner System
Lasers can provide high-speed cleaning and surface preparation in virtually all industries. This low-maintenance, easily automated process can be used to remove grease and oil, strip paint or coatings, or modify surface texture, such as adding roughness to increase adhesion.
Features:
- High-Energy Pulses: Utilizes short, high-energy laser pulses to rapidly heat and remove surface materials.
- Precision Control: Offers precise control over pulse energy, duration, and frequency to meet diverse cleaning requirements.
- Minimal Heat Impact: Minimizes thermal impact on surrounding materials, reducing substrate damage.
- Suitable for Sensitive Materials: Ideal for sensitive or fragile materials due to its precise and localized heat application.
- Effective Removal of Stubborn Contaminants: Particularly effective in removing coatings, paints, rust, and other stubborn surface pollutants.
- Ideal for Precision Components: Suitable for applications involving electronics, precision machinery, medical devices, etc. Pulse laser cleaning helps preserve the functionality and accuracy of components.


Application: Laser cleaning (rust, oil, grease, coatings, dirt, oxides, etc.)
Laser source: Pulsed fiber laser
Laser power: 100W/200W/300W optional
Applicable materials: Aluminium, stainless steel, carbon steel, stone, rubber, etc.
Pulse width: ≤20 ms
Scanning width: 0-120 mm
Repetition frequency: 20-50kHz
Voltage: 380 V/220 V, 50 Hz
Handheld Fiber Laser Cleaning Machine Price
Pulsed laser cleaners usually require higher equipment costs, as they can do zero damage to the material and are suitable for cleaning products with high demands on the surface of the substrate. Compared to pulsed laser cleaners, continuous laser cleaners have lower equipment costs and are suitable for large-scale industrial cleaning needs.
Continuous finer laser cleaner prices are usually in the thousands of dollars and upwards, while pulsed laser cleaners can range into the tens of thousands of dollars. The exact price depends on the degree of customization of the equipment, the processing capacity and the technical specifications required.
When it comes to choosing the right laser cleaning equipment, pulse and continuous laser cleaner each have their unique advantages and application scenarios. Pulsed lasers, with their high energy, short pulse widths and efficient cleaning capabilities, are suitable for treating materials with high hardness and serious surface contamination. Continuous lasers, on the other hand, with their stable power output and low energy consumption, also excel in certain applications where high cleaning speed and precision are required.