Laser cutting and engraving machines are an important part of manufacturing due to their high efficiency and precision. However, the performance and cutting quality of a laser cutting machine often depends on the condition and quality of its key components. Among these key components, the focusing lens are undoubtedly crucial link. The quality and condition of the focus lens will affects the precision and efficiency of laser cutting. Therefore, understanding what is focus lens in laser cutting machine, setting, maintain and replace focal focus lens is critical to optimizing the laser cutting.
What Does a Focusing Lens Do?
Laser utilizes a high-intensity beam to directly cut, engrave, or ablate various materials’ surfaces. In laser cutting machines, the laser beam undergoes collimation, transmission, and focusing, ultimately converging onto the workpiece to create a cutting point. The focusing lens plays a crucial role as an optical component during the laser beam transmission process.
The primary function of the focusing lens is to concentrate the laser into a focal point, ensuring a smaller focal spot and reducing the divergence angle of the light. To maintain a high transmittance, it is crucial to keep the focusing lens clean. Therefore, the cleanliness of the focusing lens is of utmost importance for the transmission and focusing effects of the laser. Short-focus focusing lenses can shorten the distance between the cutting head and the material, making it more susceptible to the intrusion of molten residue into the laser head.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Focusing Lenses
Removing the focusing lens: Extract the focusing lens from the mirror frame of the laser cutting machine, loosen the fastening screws, and sequentially remove the nozzle and the lens tube.
Dust removal: Gently blow away the dust on the surface of the focusing lens using a compressed air bulb. Ensure the use of clean gas to prevent contamination, as the surface of the focusing lens is highly sensitive to certain pollutants and moisture. Additionally, scratches and oil stains can cause serious damage to the lens.
Careful cleaning: The surface of the focusing lens may have an antireflection coating; do not handle it directly with your hands. If cleaning is necessary, use laboratory-grade soft cotton balls dipped in an appropriate amount of acetone or high-purity alcohol.
Gentle wiping: Wipe the lens gently in a clockwise direction from the center towards the edges. Ensure that the wiping material used is of optical grade to prevent damage to the lens from other contaminants.
Note on wiping tools: Use clean wiping paper, cotton balls, lens tissue, cotton swabs, or similar tools, which must be moistened with an appropriate solvent and should not be used dry.
Reassemble lens tube and nozzle: After cleaning, reassemble the lens tube and nozzle, adjust the focal distance, ensure the convex side is facing downward, and securely tighten the fastening screws.
- The slag from cutting causes auxiliary air to be blown downward from the cutting nozzle to minimize damage to the lower portion of the focusing lens from the slag.
- Avoid frequent use of ultra-high-speed piercing as much as possible.
- Perform a cleaning and maintenance before each start-up job, checking the focusing lens and laser head to make sure they are free of all kinds of contaminants and dust particles. If any abnormalities are found, the lens needs to be cleaned immediately.
How to Replace Focusing Lens for Laser Cutting?
The focusing lens of the laser cutting machine is a consumable item. If you find the lens heavily contaminated and unable to be cleaned, or if it is damaged, it is necessary to replace the focusing lens.
During laser cutting, prolonged use of the laser cutting machine’s focusing lens may result in indentations, film peeling, scratches, etc., significantly reducing the cutting efficiency of the laser equipment. So, how to replace the focusing lens:
1. Place the protective film of the laser cutting machine’s focusing lens in the palm of your hand, ensuring that the convex side of the lens is facing up.
2. Carefully pick up the focusing tube and place it in the hand with the lens, covering the entire lens completely. Keep the lens surface clean, without any stains or fingerprints.
3. Simultaneously use both hands to rotate the focusing tube 180 degrees clockwise, ensuring the correct installation direction.
4. After releasing the lens, use a small steel ruler to tighten the lens nut. Insert the ruler into the slot, gently rotate to tighten, ensuring that the edge of the ruler does not touch a part of the lens.
5. Install the air nozzle cup on the focusing tube of the laser cutting machine to maintain cleanliness and stability.
6. Gently shake to ensure that the lens is securely fastened and does not loosen.

How to Set Up the Laser Focusing Lens?
The configuration of the laser focusing lens is a crucial step to ensure the normal operation of the laser system and achieve optimal cutting results.
Preparation: Before starting the configuration, ensure that the laser cutting machine is connected and powered on, and the system is in normal working condition. Check if components such as the laser and lens are clean, and ensure that the laser beam path is unobstructed.
Adjusting the focal distance: Use the control panel or software of the laser cutting machine to adjust the focal distance of the focusing lens. The adjustment of the focal distance depends on the thickness of the cutting material, and different applications may require different focal distances.
Focus testing: Perform focus testing to ensure the accuracy of the focal point. This can be done by conducting a brief cutting test on scrap material. Observe the cutting results to ensure clear and high-quality cutting lines.
Inspecting the laser spot: Use a spot detector or other suitable methods to examine the shape and size of the laser spot. Ensure that the spot is focused at the ideal position without defocusing or over-focusing.
Optimizing cutting parameters: Based on the results of the focus test and actual cutting requirements, adjust the cutting parameters of the laser cutting machine, including laser power, cutting speed, etc.
Height of the laser head: The ideal distance between the focus and the material depends on various factors such as the type of laser used, material thickness, and so on.
Why Do the Focusing and Collimating Lenses of Laser Cutting Machines Get Damaged or Contaminated?
The focusing and collimating lenses of laser cutting machines are often contaminated primarily because the laser cutting process generates a significant amount of splatter. The high energy of the laser focusing lens means that even tiny dirt particles can lead to lens contamination. To prevent this, it is recommended to use protective gas during laser cutting, ensuring an adequate gas flow while maintaining the cleanliness of the gas and avoiding contamination by water or oil.

What is the Difference between a Focusing Lens and a Collimating Lens?
A focusing lens and a collimating lens are two different components in a laser system. The focusing lens converges the laser beam onto a small focal point for cutting, while the collimating lens reduces the divergence angle of the beam, straightening the divergent laser beam to make it parallel.
Is the Focusing Lens of Laser Cutting Machine Concave or Convex?
The focusing lens of a laser cutting machine uses a convex lens to focus the parallel laser beam onto the material being cut, based on the principle of melting cutting. The shape of the focusing lens is typically flat on one side and convex on the other, so it should be oriented with the convex side facing upward.
What Material is used for Focusing Lens of Laser Cutting and Engraving Machine?
The focusing lens of a laser cutting machine is typically made from special materials such as optical glass, or the focusing lens material may be ZnSe. Different materials have varying levels of absorption and reflection of laser energy. Therefore, the chosen lens material should be compatible with the material being cut to ensure optimal performance and prevent damage to the lens.
How often Should the Focusing Lens Be Replaced?
There are two types of lenses, protective lenses, and focusing lenses. Each protective lens typically lasts for about 200 hours of work, and they are usually replaced every 7 days in practical use. Focusing lenses, on the other hand, last for about 2400 hours of work and are generally replaced every 3-6 months in practical use.
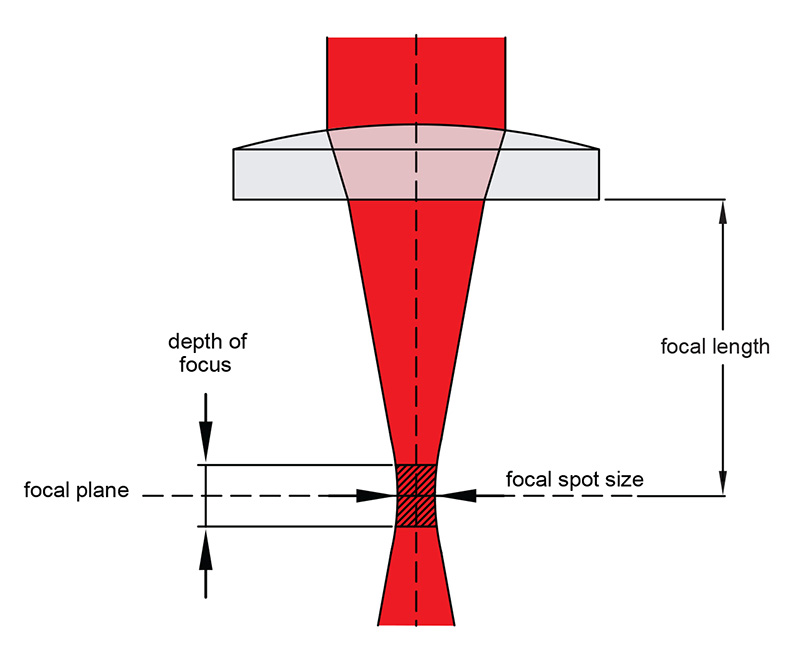
How to Choose the Focusing Lens for Laser Cutting?
The smaller the focal length of the focusing lens, the smaller the diameter of the focused spot (resulting in higher energy density at the focus), and the shallower the focal depth. When cutting thick plates, a shallow focal depth can significantly impact cutting quality, leading to burrs and rough edges. For high-speed cutting of thin materials, a short-focus focusing lens is suitable, while cutting thick workpieces is better achieved with a long-focus focusing lens.
Focusing with a short-focus lens forms a small spot, increasing the power density at the focus and accelerating cutting speed, which is advantageous for material cutting. However, the drawback is the shorter focal depth, particularly challenging to achieve evenly wide cuts, especially in thick plate cutting, affecting the quality of the kerf. Therefore, this method is more suitable for high-speed cutting of thin materials.
In contrast, a long-focus lens has lower power density at the focused spot but offers a larger focal depth, making it suitable for cutting thick workpieces as long as the power density is sufficient. This method is more practical when cutting medium to thick materials.
The Cutting Effects of Different Focusing Lenses
The laser cutting machine focusing lens has a significant impact on cutting results. To maintain cutting quality stability, it is essential to recheck and adjust cutting parameters after replacing the focusing lens, ensuring an improvement in cutting efficiency and effectiveness.
Impact on cutting depth: Replacing the focusing lens will affect the depth of laser cutting. Using a shorter focal length lens can increase laser energy density, thus enhancing cutting depth. On the other hand, using a longer focal length lens reduces energy density, resulting in a decrease in cutting depth. Therefore, when replacing the focusing lens, the choice should be made based on the cutting depth requirements, and corresponding adjustments to cutting parameters may be necessary.
Impact on cutting accuracy: Lens replacement may alter the size and shape of the focused spot, affecting the accuracy of laser cutting. To ensure cutting precision, it is necessary to recheck the accuracy of laser cutting after replacing the focusing lens and potentially adjust cutting parameters.
Impact on cutting speed: Replacing the focusing lens may influence cutting speed. Using a smaller focusing lens can reduce the cutting area, leading to increased cutting speed. However, the increase in cutting speed must be matched with control over cutting quality to avoid compromising cut quality and stability.
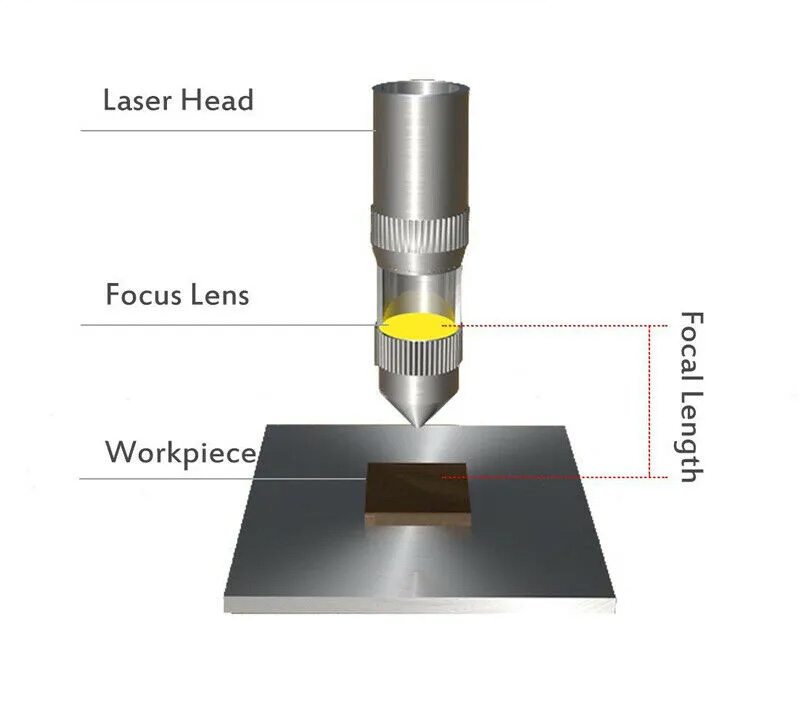
Laser Cutter Lens Focal Length
Different sizes of focusing lenses are suitable for various laser cutting and engraving requirements.
- 1.5-inch lens offers the highest resolution and is particularly suitable for cutting thin materials and engraving small details. However, it is prone to defocusing.
- 2.0-inch lens achieves the best overall performance, striking a balance between focal clarity and engraving depth. It is suitable for cutting and engraving relatively thick materials.
- 3.0-inch lens is most suitable for cutting thicker materials such as wood and acrylic resin.
- 4.0-inch lens has the maximum focal depth and is suitable for cutting thick materials or engraving materials with large curvatures. However, it requires a high-power laser to accommodate a very large spot size.
Finally:
In the above, we guided you on how to focus a laser cutter. Successful laser cutting systems rely heavily on the synergy of the various machine components, especially the focusing lens. The right choice of laser cutter lens focal length is essential for high-quality cutting, making it a key point for precise and efficient work. With DP Laser, you can improve your laser cutting projects! We are committed to helping you with any questions and solutions you may have about the laser cutting industry and helping your business succeed.




