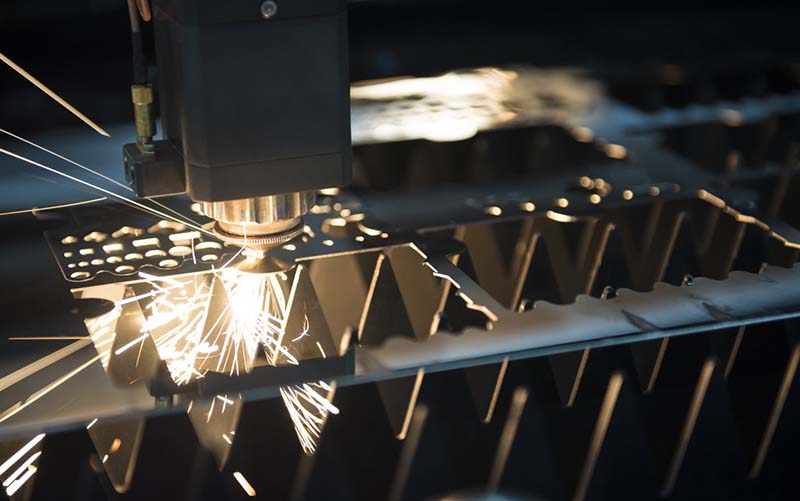
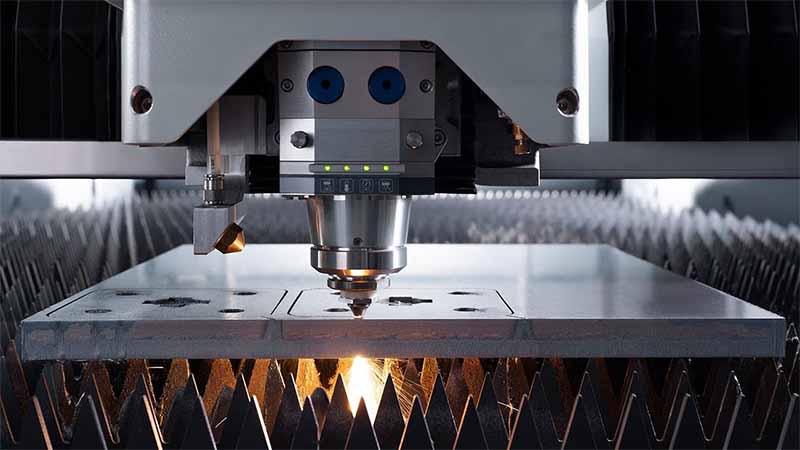
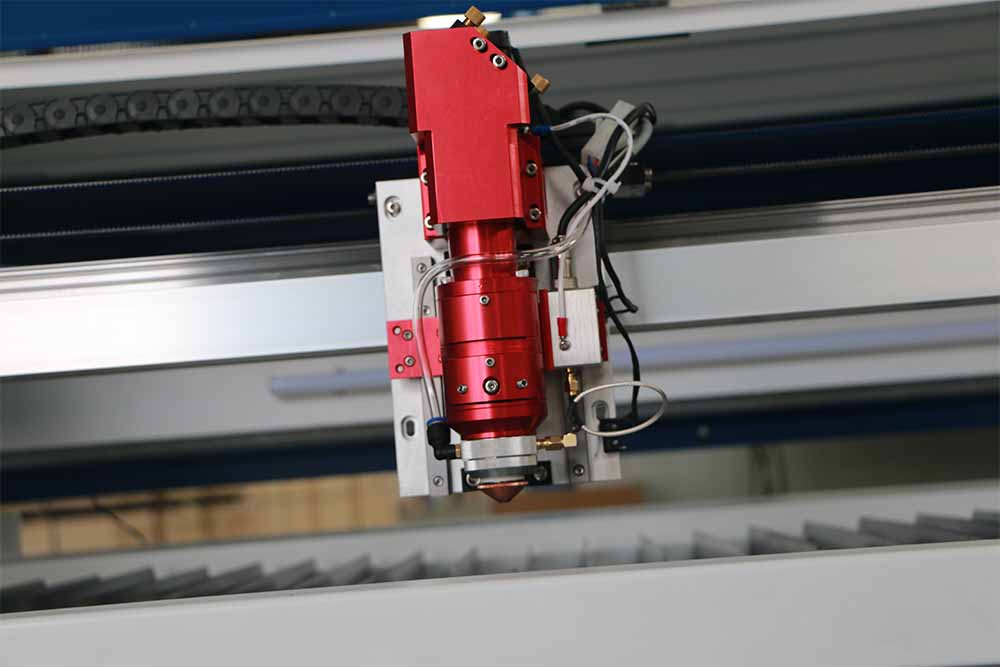
Laser cutting robot is a device that focuses a laser beam onto the surface of a material to melt it, while using compressed gas coaxial with the laser beam to blow away the molten material. It moves the laser beam relative to the material along a certain path, thereby creating specific-shaped cuts. Industrial laser cutting robots find extensive applications in processing both metallic and non-metallic materials. Using robotic laser cutting in production can significantly reduce processing time, lower production costs, and enhance the quality of workpieces.
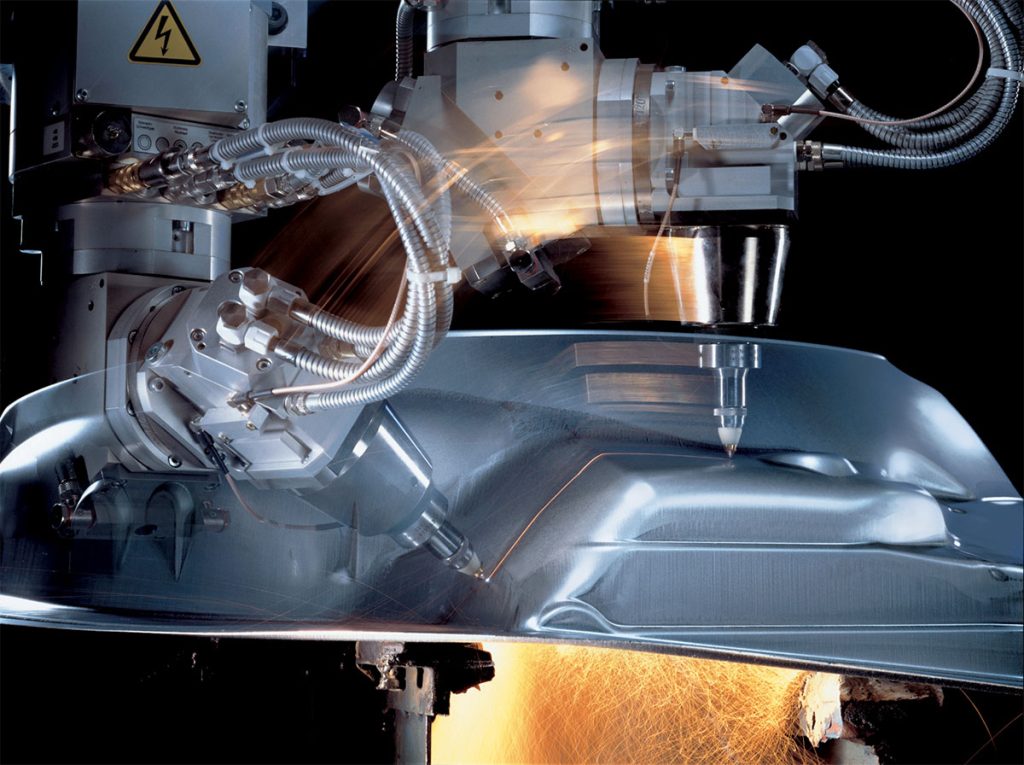
Traditional cutting processes are rather complex, involving drawing, measurement preparation, and often requiring post-cutting grinding to achieve smooth edges. In contrast, robotic laser cutting & trimming offer fast speeds and produce neatly finished edges, eliminating many cumbersome steps. This technology has gained widespread popularity in the manufacturing industry, gradually replacing or improving upon traditional metal cutting equipment.
Robotic laser cutting utilize an invisible beam of light in place of conventional mechanical blades, offering advantages such as high precision, rapid cutting, freedom from pattern limitations, automated nesting to save materials, smooth cut edges, and cost-effective processing.
Why You Need Robots for Laser Cutting?
- No Contact, No Surface Damage: The mechanical components of a laser cutting robot’s head do not make physical contact with the workpiece, preventing surface scratches during operation.
- High-Speed Cutting with Smooth Edges: Cutting robots operate at high speeds, delivering smooth and even edges. Typically, there is no need for post-processing.
- Minimal Heat-Affected Zone, Reduced Deformation: Laser cutting minimizes the heat-affected zone, resulting in minimal material deformation and narrow kerfs (0.1mm~0.3mm).
- No Mechanical Stress, No Burrs: Laser cutting leaves no mechanical stress on the material and produces clean, burr-free cuts.
- High Precision and Excellent Repetition: Laser cutting offers exceptional precision and repeatability without damaging the material’s surface.
- CNC Programming for Versatile Flat Pattern Cutting: With CNC programming, laser cutting robots can handle virtually any flat pattern, including large sheet cutting, without the need for tooling.
- Time and Cost-Efficient without Molds: Laser cutting eliminates the need for molds, saving time and reducing costs.
Robotic laser cutting is particularly suited for small-batch, three-dimensional sheet metal cutting due to its high flexibility, which manifests in two main aspects:
- Material Adaptability: Laser cutting robots can cut virtually any shape of sheet metal through CNC programming.
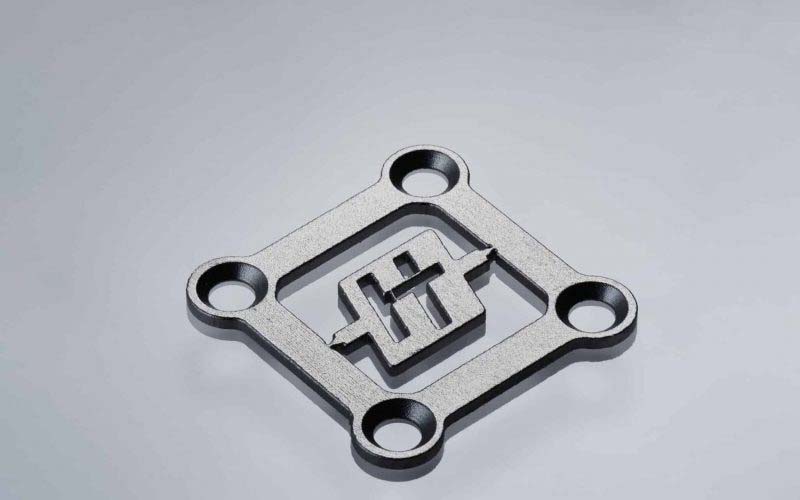
- Program-Controlled Processing Paths: The processing paths are controlled by the program. If the workpiece changes, you only need to modify the program, making it especially suitable for tasks like edge trimming and hole cutting. This trend is replacing the need for edge trimming and hole punching molds, which are often costly and limited in their applicability to different parts.
How to Choose the 3D Robot Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
The 3D robotic laser cutting system is employed for cutting three-dimensional profiles and round holes, slots, rectangles. It consists of a fiber laser source, a control system, an industrial robotic arm (typically with 5 or 6 axis), and a laser cutting head mounted at the end of the robotic arm. It represents an advanced equipment capable of multi-angle, multi-directional flexible cutting of metal sheets with varying thicknesses.
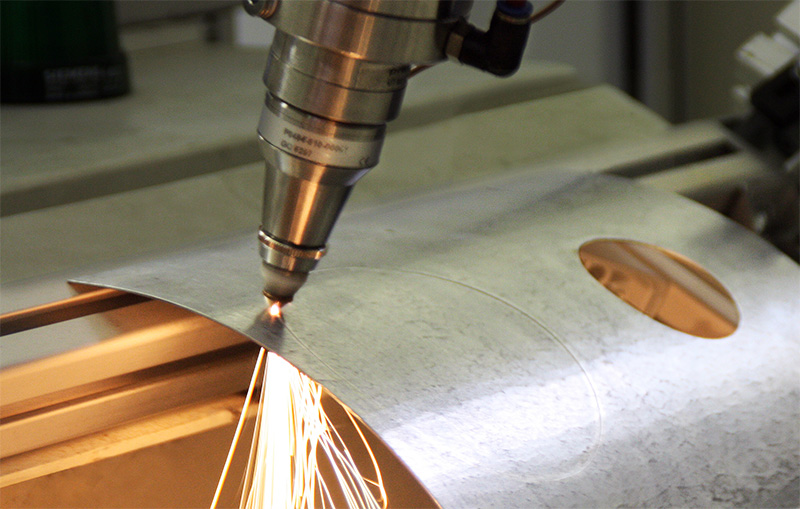

Laser Power
The power of the fiber laser can range from 1000W~6000W, offering a variety of specifications. For most applications in robot laser cutting, the thickness of aluminum and steel parts should range from 0.02 to 0.2 inches (0.5 to 5 millimeters). The cutting thickness capability depends on the laser’s performance and power.
Cooling System
Different power laser sources come equipped with varying cooling systems to ensure the proper operation of the laser. Additionally, it’s important to select the appropriate robotic arm’s working radius and fiber length based on the size of the workpiece to meet the cutting requirements.
Auxiliary Gas
Selecting the appropriate auxiliary gas for laser cutting robot system is crucial for achieving optimal results. The choice of auxiliary gas depends on various factors, including the type of material being cut, the thickness of the material, and the specific laser cutting process being used (e.g., CO2 laser, fiber laser).
Material Type:
Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is commonly used when cutting carbon steel. It provides an exothermic reaction, enhancing the cutting process.
Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen is suitable for cutting non-ferrous metals like aluminum and stainless steel. It produces a clean, oxide-free cut.
Air: For some applications, compressed air can be used, but it’s generally not recommended for high-quality cuts due to potential contamination, impurities can negatively affect the cut quality.
Six-axis Linkage Robotic Arm
6-axis industrial robot arm provides increased flexibility: With 6 axis linkage, the 3D laser head can reach any orientation in space, enhancing the feasibility of complex parts. This also improves speed, as 6 axis increase the number of possible rapid paths and reduce the need for part repositioning.
A flexible industrial cutting system makes your operations more competitive and enables quick production changes or the development of new prototypes, even for small-batch production, allowing for a rapid return on investment. Furthermore, this robot cutting system leaves room for future expansion and improvements in production lines.
The use of six-axis robot laser cutting for trimming and hole punching in sheet metal parts offers significant advantages compared to traditional die stamping techniques. It streamlines the manufacturing process, substantially reduces labor costs and mold expenses, enhances product quality and value, and finds widespread applications across various industries, including metal bending, sheet and tube processing, automotive, motorcycles, kitchenware, electronics, and more.
Robot laser cutter have several advantages in metal
1. High Precision and Repetition: Robots employ precise motion control systems, enabling them to achieve high-precision cutting operations and execute the same actions repeatedly, and ensuring consistent cutting quality.
2. Efficiency and Speed: Robots in laser cutting operate at higher speeds and can optimize processing paths through programming, enhancing cutting efficiency.
3. Flexibility: Robots can adapt to various shapes and sizes of workpieces, and programmatically accommodate different cutting modes and paths to meet diverse processing needs.
4. Automation and Safety: Robots can perform fully automated cutting operations, reducing the need for human intervention, and can operate in hazardous environments, thus improving safety.
5. Data Logging and Traceability: Robots can record relevant data during the processing and can be integrated with other systems for production traceability and data analysis.
6. Material Handling Capability: Some robot laser cutting systems come equipped with additional functions such as material handling and loading/unloading capabilities. This streamlines the manufacturing process and enhances overall system efficiency.
If you require the manufacture of molds, deep-drawn parts, die-cast components, bent tubing, or the processing of materials with complex three-dimensional shapes, then the DPLASER robot cutting system is the ideal choice to enhance your competitiveness.
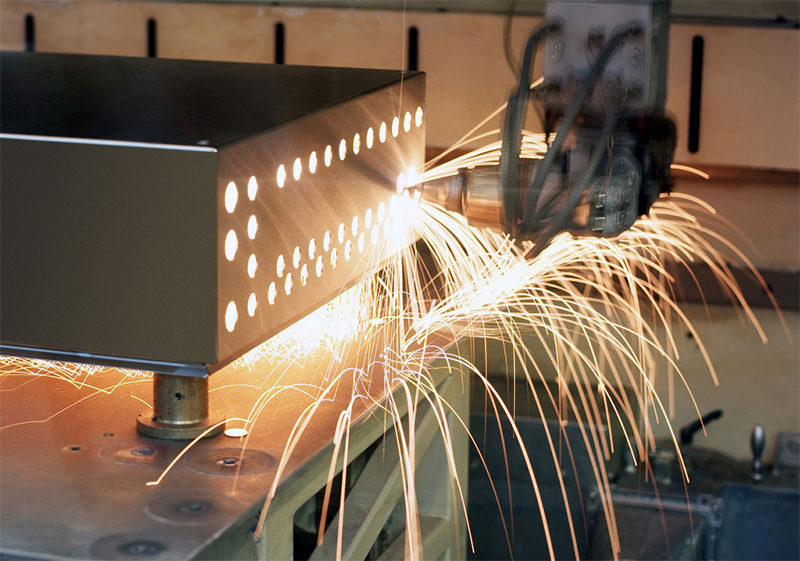

The flexible machine control system significantly reduces machine setup and estimation time, making it particularly suitable for the production of small batches of intricate workpieces. It possesses the capability to quickly adapt to changing production demands or develop new prototypes, allowing you to achieve the required output in a relatively short timeframe, thus ensuring a return on investment.
Robot for Laser Cutting Applications
The 3D laser metal cutting machine excels in precisely addressing the cutting needs of various metal materials with diverse shapes. This includes curved metal components, round tubes, square tubes, rectangular tubes, triangular tubes, elliptical tubes, H-shaped profiles, and D-shaped profiles, among others. These machines find extensive applications in the field of metal processing and are used in the manufacturing of precision metal parts and structures across a wide range of industries, including construction, automotive manufacturing, consumer electronics, sports equipment, aircraft manufacturing, and furniture production.
Robot Laser Cutting in the Automotive Industry
Automotive and motorcycle components, such as engine covers, rear covers, radiators, bumpers, fenders, doors, chassis, castings, control arms, and rear axles, require three-dimensional cutting, including trimming and hole punching.
Brake Discs: Laser cutting robots are employed for cutting and processing motorcycle brake discs. This demands a high degree of precision in the diameter, holes, and cutting edges of the brake discs to ensure braking performance and safety. Laser cutting enables fast and precise production of brake discs.
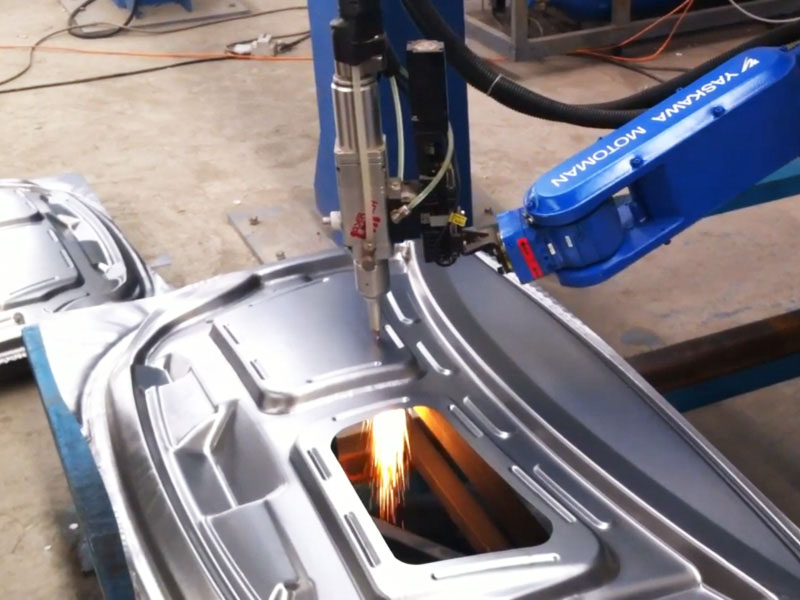

Frame Components: Motorcycle frame components often need intricate shapes and holes to provide stability and support. Laser cutting robots can cut and process these parts, ensuring their accuracy and quality while reduce model manufacturing costs and time allowing designers to implement innovative structures.

Exhaust Pipes: Exhaust pipes typically require specific shapes and holes to optimize engine performance. Laser cutting can be used to precisely cut exhaust pipes, ensuring they meet design requirements while offering the advantage of lightweight construction.
Suspension System Components: Motorcycle suspension system components, such as shock absorber brackets and suspension arms, require highly precise manufacturing to ensure ride stability and comfort. Laser cutting robots can achieve high-precision processing of these components.
Aesthetic Parts: Laser cutting robots can also be utilized to manufacture aesthetic parts for motorcycles, such as body covers and fuel tank covers. Laser cutting enables fine cutting and patterns on metal surfaces, providing personalized aesthetic designs.
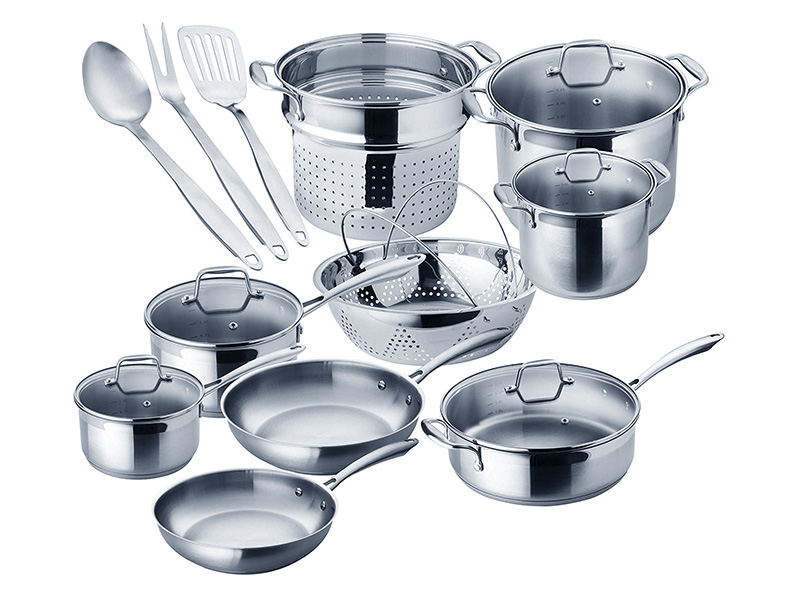
Kitchenware Manufacturing:
Cutting Stainless Steel and Aluminum Alloys: Laser cutting robots can precisely cut stainless steel and aluminum alloys for the production of kitchenware such as knives, cookware, and utensils.
Pattern and Decorative Cutting: Laser technology can be used to cut intricate patterns, brand logos, or decorations on kitchenware, enhancing the product’s appeal.

Consumer Electronics Manufacturing:
Manufacturing Electronic Casings: Laser cutting robots can be employed to cut metal or plastic casings for mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and other consumer electronic products.
Perforation and Slotting: Laser cutting can be used to create precise perforations and slots for installing electronic components and interfaces.
Precision Component Manufacturing:
Cutting Thin-Film Materials: Laser cutting robots can accurately cut thin-film materials such as circuit boards, conductive films, and sensors.
Manufacturing Micro Parts: For the production of highly precise micro parts, laser cutting is a viable choice.
Metal Sheet Tube Building Materials
Laser cutting robots have a wide range of applications in the metal sheet building materials processing industry. They are capable of delivering high-quality cutting and customized designs, facilitating the fulfillment of diverse project requirements, boosting production efficiency, and providing a variety of building materials and components for the construction industry.
With the continuous improvement and development of laser and CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technologies, robot laser cutting has emerged as an advanced method for cutting industrial sheet metal. Cutting robots are frequently employed in industrial production, and based on their different functionalities and working principles, they can be categorized into flame cutting robots, plasma cutting robots, laser cutting robots, waterjet cutting robotic, and more. Among the various cutting robots, robotic solutions for 3D laser cutting stand out for their exceptional efficiency and cutting precision.



