As a critical production process, welding directly impacts product quality and market competitiveness. Therefore, understanding how to correctly use a handheld fiber laser welding machine becomes essential in improving production efficiency and product quality. This article will provide you with a comprehensive tutorial about how to use laser welding machine for beginners. Whether you are a newcomer to laser welding or an experienced professional in the welding field, this article will offer valuable knowledge and practical guidance.
Steps to Operating a Laser Welding Machine
Preparations before Powering On:
1. Check the appearance of the laser welding machine, ensuring it is clean with no dust, oil, or debris accumulation.
2. Check the cooling system: Ensure the cooling water level is within the normal range and keep it clean.
3. Check the argon gas: Make sure the argon gas is properly connected and open.
Powering On:
1. Turn on the power supply.
2. Turn on the water chiller, laser generator, and other necessary components in sequence.
3. Open the protective gas valve and adjust the gas flow rate accordingly.
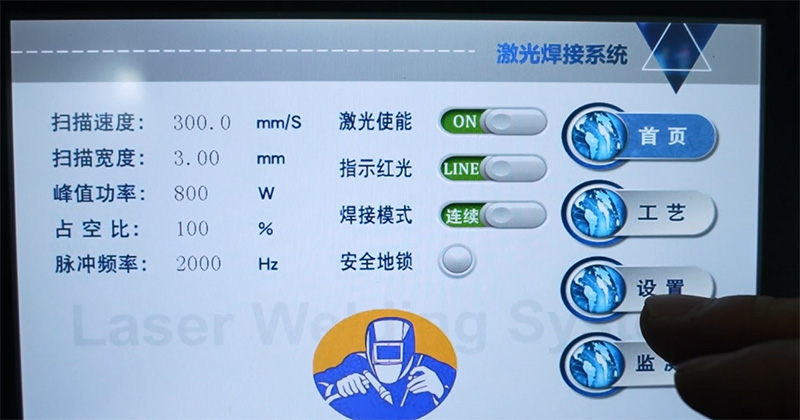
4. Select the appropriate mode and input the required parameters based on the workpiece to be welded.
5. Execute the welding operation.
Shutdown Procedure after Using the Handheld Welding Machine:
1. Exit the program and turn off the laser generator.
2. Turn off the dust collector, water chiller, and other related equipment in sequence.
3. Close the valve of the argon gas cylinder.
4. Turn off the main power switch.

Guide to How to Use a Laser Welder
Preparation: Firstly, clean and prepare the workpiece to be welded. Clean the metal surface to ensure there is no paint, debris, or rust, ensuring welding quality.
Workpiece Positioning: Place the workpiece to be welded in the appropriate position and use fixtures or positioners to secure it in place for stability. Before starting the laser welding process, ensure they are firmly clamped into position. Improper placement or alignment may result in poor welding effects.
Setting Welding Parameters: Determine the appropriate welding parameters, such as laser power, pulse frequency, focal length, etc., based on welding process requirements and material characteristics.
System Calibration: Connect the laser welding machine to the power source and perform system calibration. Ensure that all equipment and sensors are operating properly. Adjust the beam power and conduct tests on scrap materials and test pieces.
Alignment of Welding Points: Use appropriate alignment methods to align the laser beam of the laser welding machine with the welding position.
Start Welding: Press the start button or trigger to activate the laser welding machine and initiate the welding process. The laser beam will focus on the welding points, heating and melting the metal.
Control the Welding Process: During the welding process, maintain the relative position stability between the workpiece and the laser welding machine to ensure welding quality. Welding parameters can be adjusted as needed.
Complete Welding: When the welding is completed, stop the operation of the laser welding machine. After welding, let the parts cool naturally, or you can use water quenching or other cooling methods.
Inspect Welding Quality: Conduct a welding quality check, including weld quality, welding strength, welding deformation, etc. After metal connections, the welded area may require some post-processing. You can grind or polish the material to remove rough edges.
Cleanup: Clean the welding area and properly dispose of any waste or fumes generated during the welding process.

Safety Precautions for Handheld Laser Welding
1. Avoid laser eye injury, and on-site operators must wear laser-specific protective eyewear.
2. Avoid laser skin burns, direct exposure of the skin to the laser can cause burns, so on-site operators should wear work clothes to reduce the impact of diffuse reflection.
3. Carefully read the user manual and strictly follow the operating procedures for the laser welding machine to ensure equipment and personal safety.
4. Check if all parts of the welding machine are working properly. Before welding, check if all parts of the laser welding machine are working properly. After the operation, inspect the welding machine and the work area to eliminate potential hazards and ensure safety without accidents.
5. Avoid laser radiation causing fires. Direct laser beam exposure or strong reflection can cause combustible materials to ignite, leading to fires.
6. The circulating water in the laser welding machine must be kept clean; otherwise, it will affect the output of the laser. The replacement cycle of cooling water can be determined based on the operating time, water quality, and other conditions. Generally, the water replacement cycle is shorter in summer than in winter.
7. The casing of the laser welding machine must be grounded safely. During operation, never stare directly at the laser beam with the eyes, and do not let the body (such as hands) come into contact with the laser beam to avoid injury.
8. Pay attention to maintaining a clean environment and the laser welding machine. Regularly inspect whether the laser rod and optical components are contaminated.
9. If it is necessary to repair the laser welding machine, be sure to turn off the power and make sure that the stored energy capacitors have been completely discharged before proceeding to prevent electric shock accidents. If any abnormal phenomena occur during operation, the power should be turned off, and the <Emergency> button should be pressed for inspection.
Self-Protecting Design of Handheld Laser Welding System
Laser Head Protection: When the laser head encounters an (E) signal or there is no data output, the system detects motor failure, and the laser head status light goes off, and the system stops sending light signals.
Welding Gun Status Protection: When the welding gun receives the conduction status and the laser head status is all normal, pressing down the trigger button can emit light.
Trigger Button Protection: This button is equipped with multiple independent circuits, which means that if any protection function is interfered with or malfunctions, releasing the trigger button can force the system to stop connecting to the laser, effectively preventing laser emission.
System Leakage Protection: The mainboard is equipped with multiple isolation protections to prevent chassis leakage, lightning, and other factors from burning the mainboard or causing interference to the mainboard.
Overheating Protection: Monitors the internal temperature of the laser welding machine. When the temperature exceeds the set threshold, it will automatically stop working to prevent the machine from overheating and damage.
Leakage Protection: Monitors whether there is leakage in the laser welding machine. When leakage is detected, the power will be cut off to ensure the user’s safety.
Water Cooling Protection: For laser welding machines that use water cooling systems, a water temperature protection function is set. When the water temperature is too high or the water flow is blocked, it will automatically stop working to prevent damage to the fiber optic or other components.
Shielding Gas in Handheld Laser Welding
In the process of laser welding, the use of protective gas is crucial as it creates a protective atmosphere in the welding area, preventing the molten pool and weld from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements in the surrounding environment. This helps reduce oxidation and contamination, ensuring welding quality.
In handheld welding processes, the commonly used protective gas is inert gas, with argon being the most common choice.
Argon is a colorless, odorless, and non-toxic gas with excellent inert properties, meaning it does not chemically react with most metals. As a result, it is widely used for welding stainless steel, aluminum, nickel alloys, and other metals. In handheld welding machines, argon is typically jetted out near the welding head through a nozzle or gun to envelop the welding area, creating a protective atmosphere.
There are two main methods for using auxiliary gas:
1. External Jetting: Protective gas is jetted out from a nozzle or gun near the laser welding head, enveloping the welding area. This method is suitable for manual welding or cases requiring a larger jetting volume.
2. Internal Jetting: Protective gas is jetted out from inside the laser welding head, directly protecting the molten pool and weld. This method is suitable for automated welding or cases requiring more precise protection.
The flow rate and pressure of the protective gas need to be adjusted and optimized according to specific welding conditions and requirements. Welder using handheld welding machines should ensure the correct setup and use of protective gas to achieve high-quality welding results.
What Materials Can the Handheld Laser Welding Machine Weld?
Handheld Laser Welding Machine Metals: Aluminum, copper, brass, steel, titanium, and nickel, as well as various metal alloys.
Plastics: Thermoplastic plastics such as polycarbonate, nylon, and ABS.
Ceramics: Ceramic materials like alumina and zirconia.
Composite Materials: Composite materials such as carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP).
It is important to note that different types of materials may require different laser powers and parameters to achieve effective welding. Some highly reflective materials (such as silver, copper, etc.) or transparent materials (such as glass) may pose challenges in laser absorption and welding. Additionally, for complex material structures or combinations, specific nozzle and process controls may be needed to achieve the desired welding results.
Therefore, before choosing the proper laser welding for a specific material, it is recommended to conduct experiments and tests based on the properties and requirements of the material to determine the most suitable welding parameters and methods.

Transportation Precautions
1. Proper Packaging: Before shipping, ensure that the handheld laser welding machine is adequately packed with wooden frames and foam protection to prevent damage or collision during transit.
2. Moisture Protection: Take appropriate measures to prevent moisture or water damage during transportation, especially for sea transportation.
3. Secure on the Ship: Arrange the equipment in an appropriate position on the ship and use firm supports and restraints to prevent shaking and sliding during the journey.


Installation and Debugging Precautions
1. Environmental Check: Ensure that the welding machine is installed on a stable ground or support, in a dry and well-ventilated environment, and avoid dust and foreign objects from entering the equipment.
2. Power Requirements: Check the power requirements of the welding machine and ensure that the appropriate power voltage and current are provided.
3. Gas Source Preparation: If necessary, prepare the required protective gas and ensure a stable gas supply.
4. Safety Measures: Familiarize yourself with the safety operation manual of the welding machine before commissioning, and wear necessary personal protective equipment.
5. Parameter Settings: Set appropriate laser welding parameters, such as power, frequency, focal point position, etc., according to the welding task requirements.
6. Install Cooling System: Install the cooling device to cool the laser source. Connect the cooling system to the laser source using the correct accessories and pipes provided in the installation kit. Ensure all connections are secure and reliable. Connect all electrical and air connections to the machine and ensure their wiring and layout are correct. It may be necessary to hire an electrician or technician to handle electrical connections.
7. Welding Test Samples: Conduct welding test samples before formal welding to confirm that the welding quality meets the requirements.
8. Quality Inspection: During the commissioning stage, regularly inspect the welding quality and weld appearance, and make timely adjustments to parameters and equipment.
9. Operator Training: Ensure that the operators are familiar with the operation and safety procedures of the handheld laser welding machine and train them in the correct operation of the equipment.
10. Maintenance Plan: Develop a regular maintenance plan to keep the equipment in good condition and extend its service life.
Laser equipment suppliers will provide complete product debugging services, live training and after-sales support and other professional services during the sales process to ensure that customers get the best experience and after-sales support to realize efficient production and sustainable development. So you don’t need to worry too much about using the hand held laser welder.
Disadvantages of Hand-held Laser Welding Machine
Laser welding is a high-precision and high-efficiency metal welding method, but it also has some limitations.
1. Material selection limitations:
Hand held laser welding is suitable for most metals and alloys, including steel, aluminum, copper, etc. However, certain materials, such as highly reflective materials (e.g., silver, copper) or transparent materials (e.g., glass), have strong reflection or transmission of laser beams, making welding difficult.
2. Thick plate limitations:
Handheld fiber laser welding is suitable for thinner metal sheets, and welding thicker materials may require additional steps or changes in welding parameters to avoid reduced welding quality or deformation.
3. Higher equipment cost:
Handheld laser welding equipment, including laser sources, fiber optic transmission systems, and welding heads, can be relatively expensive. For some small-scale or low-budget applications, laser welding may not be the most economical choice.
4. Welding speed limitations:
Compared to other welding methods, hand-held laser welding is slower and is more suitable for small-scale complex tasks. Although laser welding requires less post-processing and cleaning compared to other types of welds, the slower welding speed may limit its use in large-scale production or high-volume applications.
5. Welding scan range limitations:
The welding area in laser welding is limited by the scanning system, and the welding size and shape are restricted by its scanning range. For some complex or very large workpieces, additional process control and operations may be needed.
Despite these limitations, laser welding remains a widely used advanced welding method in many application fields due to its high precision, high quality, and controllability. It plays a significant role in industries such as automotive manufacturing, electronics, aerospace, and others. With technological advancements, efforts are continually being made to overcome and improve the limitations of laser welding.
Welcome to DP laser most comprehensive tutorials on how to operate your handheld welding machine! We provide product introduction, using steps, parts introduction, installation and replacement, software introduction, welding method instruction as well as common troubleshooting and solutions. For more video tutorials on handheld laser welding, please visit DPLASER welding YouTube channel.
Finally, in practical operation, it is essential to follow the handheld laser welding machine tutorial provided by the manufacturer for the particular model Always ensure that the correct operating procedures and safety standards are followed during installation and debugging. With the continuous development of manufacturing market and increasing competition, mastering the correct usage of the handheld laser welding system will become a powerful tool for you to stand out in the industry.