Laser Welding Aluminum Alloy
Applications of Laser Welding Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are widely used in the production of various products such as containers, machinery, electrical equipment, chemical components, and aerospace structural parts due to their characteristics of lightweight, high toughness, high yield ratio and ease of processing and forming.
Laser welding is widely utilized for joining aluminum alloy components, including automotive body parts, doors, hoods, and chassis, electronic components, the shells, brackets, and connecting parts of medical equipment, aluminum alloy windows, door frames, enclosures, elevator components, water pipes, and more.
Laser welding has found widespread applications on these aluminum and aluminum alloy materials to achieve high precision and efficiency in welding processes.
Laser welding is commonly used for the following aluminum and aluminum alloys:
1. Pure Aluminum (1xxx Series): Pure aluminum is one of the easiest aluminum materials to laser weld. It is typically used in applications with low strength requirements, such as food packaging and electronic components.
2. Aluminum Alloys: Aluminum alloys are formed by alloying aluminum with other elements such as copper, magnesium, silicon, and zinc to achieve various properties.
- 7075 Aluminum Alloy (7xxx Series): Used in bicycle and motorcycle components such as brakes, frames, wheels, and other parts due to its lightweight and robust nature, capable of withstanding rigorous use.
- 6061 Aluminum Alloy (6xxx Series): Known for its excellent strength and corrosion resistance, it is commonly used in aircraft structures, wings, fuselages, propellers, engine components, and automotive parts.
- 6063 Aluminum Alloy (6xxx Series): Often used in the structural components of windows, door frames, and curtain walls.
- 5083 Aluminum Alloy (5xxx Series): Used in shipbuilding and rail transportation due to its outstanding corrosion resistance and resistance to seawater corrosion.
- 3003 Aluminum Alloy(3xxx Series): Due to its good formability, it is commonly used in food packaging and containers, such as cans, beverage cans, and food boxes.
- Other type of aluminum alloys: Some aluminum alloys to meet specific application requirements.
In welding different aluminum alloys, it is essential to employ appropriate process, select the right welding method, and use the correct filler material to achieve sound welding joints.





Advantages of Laser Welding for Aluminum
Laser welding provides exceptional precision and accuracy. The focused laser beam can be precisely controlled, allowing for tight tolerances and fine weld seams, making it suitable for applications requiring intricate or small welds.
Laser welding is a high-speed process. The concentrated energy source allows for rapid heating and cooling, welding speed is 3 to 5 times compared to traditional argon arc welding.
Laser welding can be used for a wide range of aluminum alloys, including those with different thicknesses and properties. It can handle various joint configurations, making it versatile for diverse applications.
Laser welding produces clean, aesthetically pleasing welds with minimal spatter, oxidation, or defects.
Laser welding generates minimal contamination, as there is no need for consumable filler materials or fluxes. This is crucial when welding aluminum, as it reduce external impurities to enhance welding strength and quality.
Laser welding is a non-contact process, this eliminates the risk of mechanical damage to sensitive components.
Laser welding can be easily automated and integrated into production lines. This reduces labor costs, ensures consistency, and enhances overall manufacturing efficiency.
Laser-welded joints typically require minimal post-processing, as the welds are clean and precise.
| Argon Arc Welding VS. Laser Welding | ||
| Items | Argon Arc Welding | Laser Welding |
| Heat | High heat | Low heat |
| Deformation | Prone to deformation | Minimal or no deformation |
| Weld Bead | Large weld bead | Smaller weld bead, adjustable spots |
| Aesthetics | Requires processing, high grinding costs | No need for post processing and low processing costs |
| Penetration | Susceptible to perforation | Not prone to perforation |
| Shielding Gas | Requires Argon gas | Requires Argon/Nitrogen gas |
| Precision | traditional | High precision, Computer numerical control (CNC) |
| Efficiency | traditional | 2-5 times faster |
| Safety | Intense ultraviolet radiation | Safe irradiation, almost no harm |
| Skill Requirements | Skilled welders | No technical requirements |
Laser Welding Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys Samples
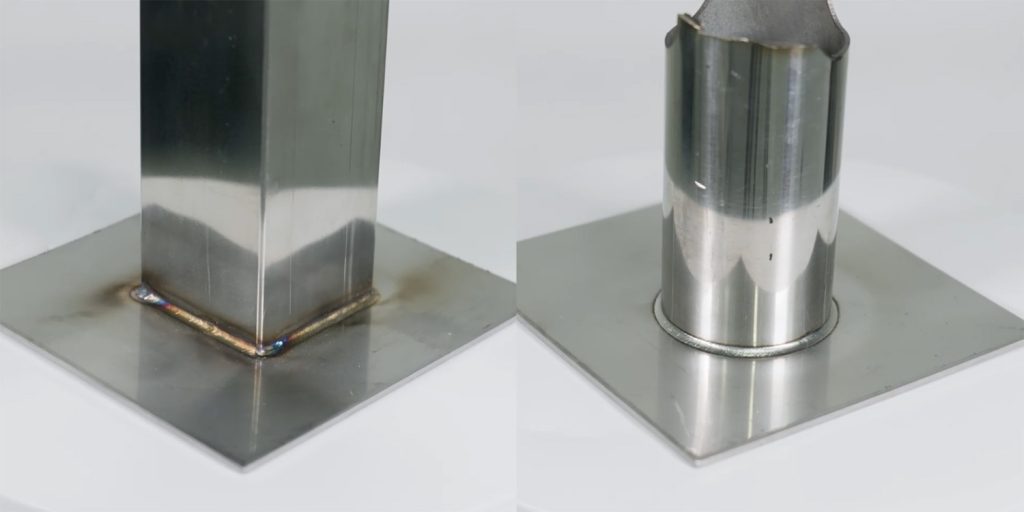





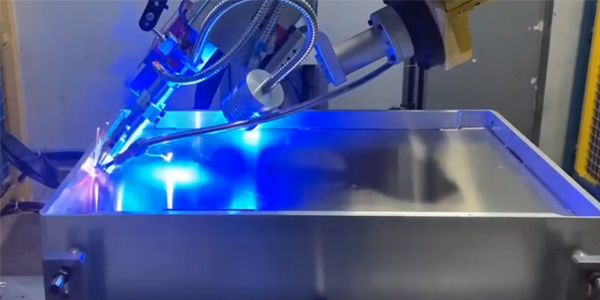


Laser Welding Aluminum Parameter
| Material | Gas used | Thickness(mm) | Laser power(W) | Wire diameter(mm) | Wire speed(mm/s) | Scanning speed(mm/s) | Scan width(mm) | Welding frequency(HZ) | Duty cycle |
| Aluminum | Nitrogen(N2) | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 90 | 300 | 2.5 | 1000Hz | 100% |
| 1.5 | 1500 | 1 | 90 | 300 | 2.5 | 1000Hz | 100% | ||
| 2 | 2000 | 1.2 | 75 | 300 | 2.5 | 1000Hz | 100% | ||
| 2.5 | 2000 | 1.6 | 60 | 300 | 3 | 1000Hz | 100% | ||
| 3 | 3000 | 1.6 | 60 | 300 | 3.5 | 1000Hz | 100% |
GET YOUR SOLUTIONS
Get a Free Quote
Share your needs, and our professional engineers will offer tailored machines and free quotes for your business.
Contact Us
Welcome to DPLaser to experience and learn to use laser equipment.
Live Chat
We are always here!